Stem cells are powerful cells that can transform into new specialized types, replacing old or damaged cells. When it comes to repairing a joint, stem cell therapy has shown improvement in treatments. When a bone loses its protective covering called the articular cartilage, osteoarthritis can result.
This painful, degenerative disease causes stiffness, swelling, and mobility problems. But stem cells could be the key to delaying or preventing it altogether. It’s been suggested that stem cells injected into a joint could alter damaged cartilage and repair it.
What is Stem Cell Treatment?
Stem cells are naturally occurring cells that can transform into other cell types. They are present in almost every tissue, although they have unique properties that make them particularly useful for treating damaged tissue. Stem cells can be isolated from the bone marrow, brain, and skin.
Stem cell treatments work by stimulating stem cells in the patient’s body to differentiate and multiply into specific cell types required for tissue repair. This type of stem cell is usually present in the patient’s bone marrow, but different kinds of stem cells are available. Platelet-rich plasma is one of the most promising but is currently said to be effective in improving non-complicated knee osteoarthritis.
Types of Stem Cells
1. Embryonic Stem Cells
Embryonic stem cells are derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst-stage embryo. This is the earliest stage of development when the organism is just a cluster of cells. Embryonic stem cells are totipotent, meaning they have an enormous capacity for differentiation and can develop into any cell. If used in regenerative medicine, embryonic stem cells could be used to replace damaged tissues and organs.
2. Adult Stem Cells
Adult stem cells are present in many body organs and tissues and can renew through cell division. These cells are multipotent, which means they can only generate a limited number of cell types. This makes adult stem cells more restricted in their differentiation potential than embryonic stem cells, but they also become specialized more quickly than embryonic stem cells. They are found in fully developed tissue such as skin, bone marrow, and brain.
Stem Cells in Medicine
Stem cells used to treat disease are obtained from a patient’s bone marrow. This can be extracted with a needle in the bone, but more commonly, small samples are removed through minimally invasive surgery. Fibroblast cells are then isolated from these samples and cultured in a laboratory until they can become specialized and mature.
The tissues are sometimes grown on plastic culture dishes in a laboratory, but more commonly, they are taken from the patient’s body. These tissues or cells can then be used to treat damaged tissue or repair disease by introducing them into the body.
Areas Where Stem Cell Therapy Can be Used
Stem cell therapy can treat many conditions, including burns and skin injuries, multiple sclerosis, lupus, and neurological. It’s also been used to treat other diseases such as diabetes, cancer, Alzheimer’s, and heart disease. Stem cell therapy holds great promise for treating osteoarthritis.
Stem Cell Therapy for Joint Replacement
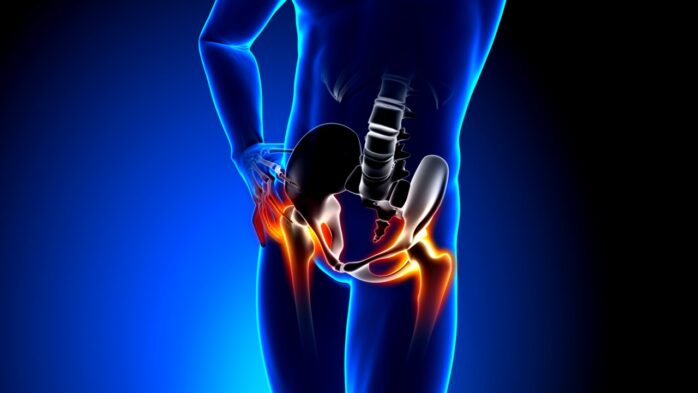
For joint replacement, stem cells have been involved in replacing bone marrow, a process already used to treat bone marrow failure. In the current clinical trials of stem cell therapy for knee osteoarthritis, patients needed stem cell injections into their knee joints at least 18 months later than conventional treatment.
The patient’s bone marrow needed time to produce the required stem cells. Stem cell therapy has also been tested in patients with knee osteoarthritis, and it has shown improvement in the patient’s ability to walk.
Where Do Stem Cells Come From?
Stem cells are only found in body areas, such as bone marrow, skin, and the brain. The best source of stem cells for treating osteoarthritis is bone marrow. This is because stem cells are found in the lining of cartilage and blood vessels in the joint.
Is Stem Cell Therapy Safe?
Most stem cell therapy that uses adult stem cells is safe because they are your cells. But the main problem is that some of these cells can transform into unwanted cell types, most commonly a type of immune cell called lymphocytes, which can lead to an autoimmune response. This means the body recognizes its cells as foreign and attacks them. To reduce the risk of this happening, stem cells are usually tested in animal models before they are used on humans.
Stem Cell Therapy Effectiveness
Researchers have found that stem cells help to reduce osteoarthritis. They reduce the inflammation that worsens the joint pain, grow into the required cartilage cells, and release the cytokines that lessen the pain.
Stem Cells and PRP
Stem cells may be used to treat knee OA with some success. Platelet-rich plasma contains an ideal mixture of growth factors and proteins that help stimulate the healing process in osteoarthritis. Stem cells are powerful in regenerative medicine because they can differentiate into any cell. PRP is obtained from the patient’s blood; platelets are rich in growth factors and proteins required for regeneration, cell division, and healing. They include platelet-derived growth, epidermal, and fibroblast growth factors. PRP is injected into the joint.
What is in a Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection?
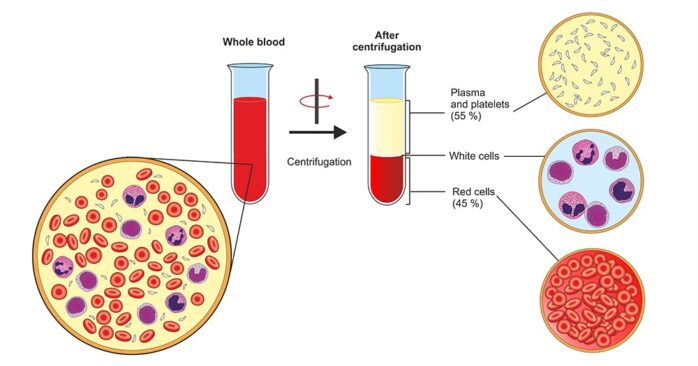
PRP contains a concentration of white blood cells, platelets, and additives.
1. Concentration of Platelets
The concentration of platelets in the PRP is higher than in normal blood. The concentration levels depend on how much blood was drawn and the method used to produce PRP by the doctor.
2. The concentration of White Blood Cells
White blood cells are a collection of immune system components. They are responsible for stimulating stem cells to repair damaged tissues.
3. Additives
Depending on its intended use, various additives can be added to the platelet-rich plasma solution. These additives include thrombin and calcium chloride, which helps the body to clot, and anti-inflammatory agents, growth factors, or cytokines such as the epidermal growth factor.
Benefits of PRP
It helps slow down knee osteoarthritis damage. PRP has rapid action and faster recovery; it accelerates blood circulation and brings blood flow to the damaged area.
Stem Cell Therapy Side Effects
While most stem cell treatments are safe, complications can arise. These include immune response, where the body recognizes the injected stem cells as foreign substances and attacks them, causing inflammation and swelling. Another side effect is a reaction from the patient’s body against proteins found in the bone marrow that could lead to a dangerous response that could affect other organs.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy is an exciting technique that is being studied for a wide variety of conditions, including arthritis. Research has shown that treating osteoarthritis with stem cell therapy can help reduce joint pain and inflammation, but there is still much more to learn about the true benefits of using this technique.